SomaScan Select 3.7K Assay
Over 3,000 protein measurements
targeting core proteins across all disease states.
Get early access now
Announcing the SomaScan Select 3.7K Assay
Now available for early access in our CAP/CLIA-accredited lab
![]()
Send samples to our CAP/CLIA-accredited lab
![]()
Receive data through our secure portal
![]()
Comprehensive data analysis tools
The SomaScan™ Select 3.7K Assay is a lower-cost, agile proteomic tool designed to empower researchers with
high-plex proteomic capabilities.
Sample types
- Available in human and non-human plasma and serum, cells and tissue
Comprehensive analysis tools
- Full suite of tools in GitHub and CRAN
- Cloud-based statistics and visualization tool available
- Custom data analysis and consultations
Upgrade option
- Researchers have the option to upgrade to a fully customized version of the assay
Featuring 3,770 unique protein targets with deeper disease area coverage than other high-plex antibody assays
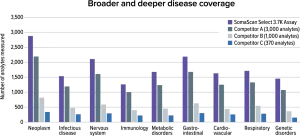
- Broad proteome coverage
- 100% of top-level pathways and 85% of all pathways in Reactome
- Common clinical marker coverage
- >70% of all FDA-approved biomarkers included
- Curated library
- 3,770 unique protein measurements chosen for diversity in measurements and extensive third-party validation
World-class performance with higher reproducibility and more KEGG pathway coverage than high-plex antibody assays
- Precision: <5% total median CV
- Signal-to-noise ratio: 99% content signal:noise >2
- Sensitivity in buffer: 187 fM median
Trusted results from Standard BioTools
With over 1,300 publications, the SomaScan Assay is a trusted choice
for reproducibility and precision
PUBLICATION
Kirsher, D. et al.
The current landscape of plasma proteomics:
technical advances, biological insights, and biomarker discovery
bioRxiv (2025)
In a peer-reviewed study, the SomaScan Platform demonstrated the best technical performance
The SomaScan Platform showed the best (lowest) technical variability and a stronger signal-to-noise ratio than other platforms.
Technical variability observed for a high-plex antibody assay and the SomaScan Platform aligns with findings from an ARIC platform comparison study (Rooney et al., 2024).
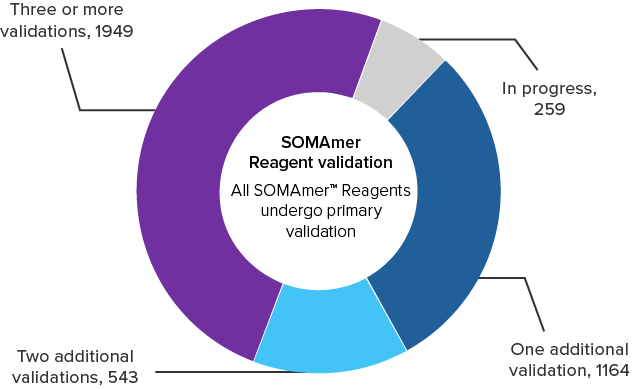
Every assay is validated by our
comprehensive primary validation steps
More than 3,770 of the SomaScan Select 3.7K Assays have at least one additional form of orthogonal validation.
Primary validation
- Determination of equilibrium-binding affinity dissociation constant (Kd)
- Pulldown assay of cognate protein from buffer
- Demonstration of buffer dose response in the SomaScan Assay
- Estimation of endogenous cognate protein signals in plasma
Uniquely addresses translational medicine needs with high signaling performance:
A new tool to accelerate therapeutic development
See how the SomaScan Assay can be leveraged in discovery through clinical development
In a recent study in Nature Medicine by researchers from Novo Nordisk, the SomaScan Assay was used to profile 1,956 patients. The data revealed unique mechanisms of action and supported drug repurposing.
Study goal
- To evaluate semaglutide’s effects on circulating proteins in serum samples from Phase 3 clinical trials, upon 68 weeks of treatment
- To compare semaglutide’s proteomic effects with proteins known to relate to a variety of disease from an external observational cohort (deCODE)
Experimental design
- Analyzed baseline and end-of-treatment serum samples.
- Step 1: 1,311 participants (overweight/obesity without diabetes)
- Step 2: 645 participants (overweight/obesity with type 2 diabetes)
- Measured thousands of proteins with the SomaScan 7K Assay
Key findings
Unique mechanistic insights: The SomaScan Assay identified semaglutide’s specific effects on proteins and pathways, revealing benefits beyond obesity.
Reliable and reproducible results: The SomaScan Assay delivered consistent, quantitative findings across Phase 3 studies, measuring proteins not detectable by other platforms.
Accelerated clinical development: The RCVR SomaSignal™ Test successfully detected semaglutide’s cardiovascular benefits, enabling earlier insights from smaller studies.





