Bring neurology discoveries to light with the SomaScan® Assay
Detect low-abundance proteins in complex sample types, including cerebrospinal fluid and blood.
Unlocking advances in neurological research
Nearly 100 million people in the United States alone suffer from one of more than 1,000 different neurological diseases.1 These diseases can derive from various sources, such as faulty genes, problems with development of the nervous system, degeneration of the nervous system, dysfunctional proteins, and signaling pathways.2-4
In neurological research and clinical settings, the use of biomarkers is crucial for a deeper understanding of the mechanisms behind these diseases and for enabling early detection. Traditionally, neurology has relied on cognitive assessments, imaging techniques, and postmortem brain tissue analysis to study disease. In recent years, proteomics, or protein profiling, has emerged as a powerful tool in neurological research. Proteomics can measure complex body fluids like cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), providing a comprehensive approach that allows researchers to accurately identify potential biomarkers. This improves knowledge of disease mechanisms and enables earlier detection and the development of targeted treatments.
The power of proteomics with the SomaScan Assay
The SomaScan Platform harnesses the power of proteomics for targeted research, facilitating the discovery of potential biomarkers and utilization as a research tool in clinical trials.
By leveraging high-content profiling, the platform can be used to further the study of a range of neurologic diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, spinal cord disorders, as well as cancer.5-9 In addition, this sensitive proteomics approach can be used to identify and track blood- and cerebrospinal fluid-based biomarkers, which can be used in research related to disease and disease progression5,10, ultimately translating to faster drug development.
CSF offers insight into neurologic disease pathology through comprehensive protein measurement

Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a critical fluid for neurological research due to its association with the central nervous system. The SomaScan 11K Assay now supports CSF samples, offering even greater precision in neurological research and biomarker discovery. By incorporating CSF samples, the SomaScan 11K Assay enables researchers to gain deeper insights into disease mechanisms and protein biomarkers specific to neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and other neurodegenerative conditions. This expanded capability accelerates advancements in neurobiology and translational research.
CASE STUDY Revealing New Insights in Parkinson’s Disease Using CSF Samples and the SomaScan Assay
This case study by Phillips et al. presents the largest SOMAmer® reagent-based proteomics analysis of CSF to date, identifying 25 proteins linked to Parkinson’s disease. The study highlights the utility of the SomaScan Assay in analyzing CSF to uncover novel protein associations, contributing to a deeper understanding of neurological disorders. Learn how CSF proteomics can enhance biomarker discovery and therapeutic research.
View full case study
Biomarker discovery and identification
with the SomaScan 11K Assay
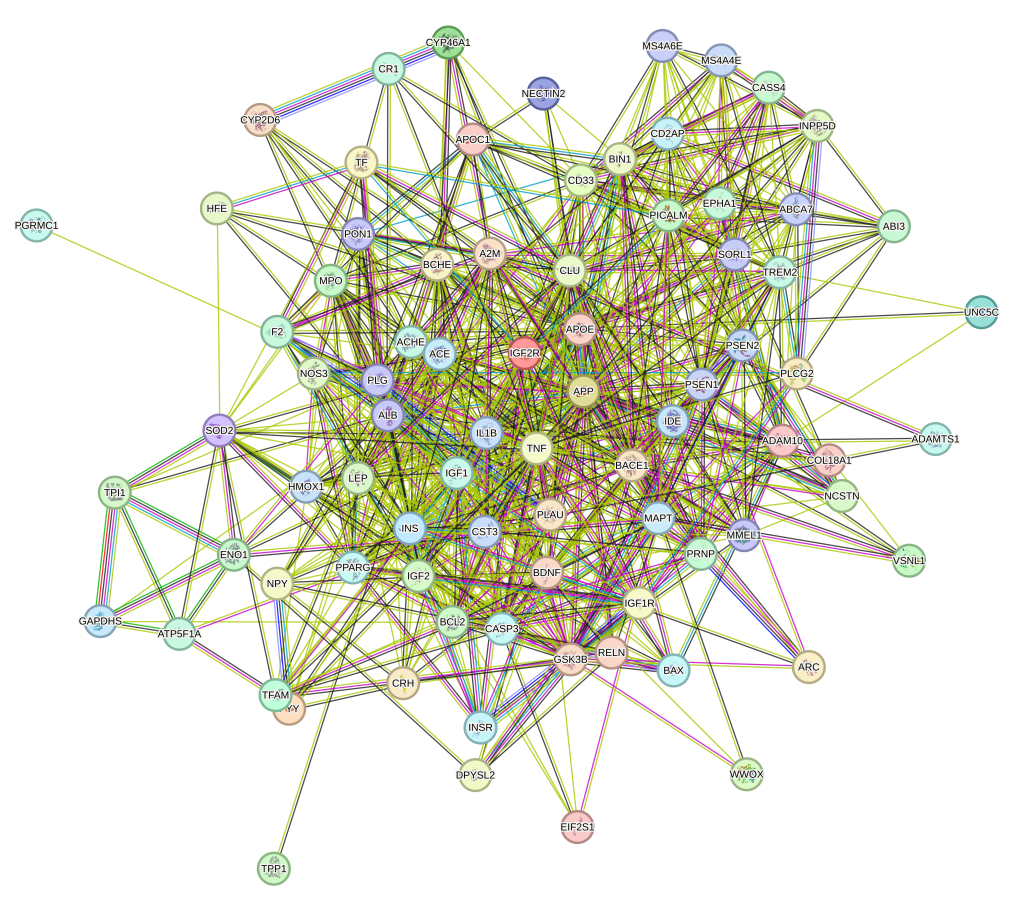
Over 3,500 protein targets associated with neurology can be measured using the SomaScan 11K Assay. This figure depicts a protein-protein interaction network of Alzheimer’s disease associated protein targets (i.e. Apo-E, Tau, BDNF) using the pathway analysis tool STRING. A comprehensive list of protein targets included in the SomaScan 11K Assay is accessible via the SomaScan Menu Tool.
Look deeper with the SomaScan Platform
Multiplex, high-throughput proteomics
Profile 11,000 protein measurements per sample and conduct high-throughput analysis of >1,000 samples simultaneously.5

Sensitive detection
Detect and quantify a wide dynamic range of proteins (from fmol – µmol) in complex sample types, including cerebrospinal fluid and blood.5,10

Reproducible
Obtain consistent and reproducible inter- and intra-assay results for data analysis and comparison.5

Using proteomics to advance understanding of alzheimer’s disease
Limited understanding due to its complex pathophysiology and lack of definitive biomarkers currently constrains the diagnosis and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). But new research is uncovering dynamic brain changes during Alzheimer’s progression, offering potential therapeutic targets. This webinar explores how proteomics and systems biology can be integrated to elucidate AD pathology.

Application Focus: Exploring Brain Diseases Through Plasma Proteomics
Keenan Walker, PhD and Chief, Multimodal Imaging of Neurodegenerative Disease (MIND), National Institute on Aging (NIH) summarizes information that explores the relationship between systemic proteins and Alzheimer’s disease in this paper. This paper is based on his presentation from the webinar titled “Using plasma proteomics to understand Alzheimer’s and other brain diseases”.

Young blood for old brains and the quest to slow brain aging
Tony Wyss-Coray, PhD, D.H. Chen Distinguished Professor of Neurology and Neurological Sciences and Director of the Phil and Penny Knight Initiative for Brain Resilience at Stanford University, presents data on his team’s findings that blood-borne factors from young humans and mice are sufficient to counteract aspects of brain aging and improve cognitive function in old mice, while blood plasma from old organisms is detrimental to young mice and impairs their cognition.
Proteomics for precision neuroscience: The power of protein analysis
Christopher Whelan, MSc, PhD, Carlos Cruchaga, PhD, and Keenan Walker, PhD, discuss how academic, industry, and government researchers are directly measuring protein abundance and function via multiplex proteomics to build more detailed characterizations of the biological systems underlying neurodegenerative diseases.
Advanced proteomics offerings in neurology
The SomaScan Platform is available in multiple formats, each providing unique data outputs to fast-track your neurology research.
SomaScan Assay
With the ability to profile thousands of proteins simultaneously, the SomaScan Assay is well-suited to measuring low- and high-abundant proteins in a small amount of blood or cerebrospinal fluid.5,10
SomaScan Panels
These custom panels can be individualized from our menu of 11,000 protein analytes. The assay is also offered as a neuroscience panel containing 1,316 preset analytes most relevant to neurology-focused proteomics. This panel focuses on significant neurologic disease associations including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, spinal cord disorders, cancer, ischemia, seizures, addiction, pain, and others.5
SomaSignal® Tests
Monitor clinical metrics, including those associated with dementia and other critical parameters, such as cardiovascular fitness and glucose tolerance.5,11
Curated neurology research publications
Additional resources
BLOGProteomic profiling in cerebrospinal fluid: advancing biomarker discovery in neurology
With nearly 100 million people in the United States alone suffering from a neurologic disease, there is an urgent need for reliable biomarkers to aid in diagnosis, monitoring, and development of new treatments.1,2White paperThe SomaScan® Assay enables discovery of blood-based biomarkers in neurodegenerative diseases
Blood-based biomarkers show promise as a minimally invasive, cost-effective option for the detection, classification, and monitoring of neurologic diseases.1-3WebinarUsing non-hypothesized based approaches for biomarker development
Current biomarkers are only moderately predictive in identifying individuals with mild traumatic brain injury or concussion. Therefore, more accurate diagnostic markers are needed for sport-related concussion (SRC).References: 1. Gooch CL, Pracht E, Borenstein AR. The burden of neurological disease in the United States: a summary report and call to action. Ann Neurol. 2017;81(4):479-484. doi:10.1002/ana.24897. 2. Moujalled D, Strasser A, Liddell JR. Molecular mechanisms of cell death in neurological diseases. Cell Death Differ. 2021;28(7):2029-2044. doi:10.1038/s41418-021-00814-y. 3. McKinnon PJ. DNA repair deficiency and neurological disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2009;10(2):100-112. doi:10.1038/nrn2559. 4. Sweeney P, Park H, Baumann M, et al. Protein misfolding in neurodegenerative diseases: implications and strategies. Transl Neurodegener. 2017;6:6. doi:10.1186/s40035-017-0077-5. 5. Data on file. SomaLogic Operating Co., Inc. 6. Ward M, Schofield EL. Biomarkers for brain disorders. Therapy. 2010;7(4):321-336. 7. Shi L, Winchester LM, Westwood S, et al. Replication study of plasma proteins relating to Alzheimer’s pathology. Alzheimers Dement. 2021;17(9):1452-1464. doi:10.1002/alz.12322. 8. Yang C, Farias FHG, Ibanez L, et al. Genomic atlas of the proteome from brain, CSF and plasma prioritizes proteins implicated in neurological disorders. Nat Neurosci. 2021;24(9):1302-1312. doi:10.1038/s41593-021-00886-6. 9. Candia J, Cheung F, Kotliarov Y, et al. Assessment of variability in the SOMAscan Assay. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):14248. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-14755-5. 10. Masvekar R, Wu T, Kosa P, Barbour C, Fossati V, Bielekova B. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers link toxic astrogliosis and microglial activation to multiple sclerosis severity. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2019;28:34-43. doi:10.1016/j.msard.2018.11.032. 11. Walker KA, Chen J, Zhang J, et al. Large-scale plasma proteomic analysis identifies proteins and pathways associated with dementia risk. Nat Aging. 2021;1:473-489. doi:10.1038/s43587-021-00064-0.




